CGinspiration
By Alfred Kammer, Director, IMF’s European Division and Luis Brandao Marques, Deputy Chief, European Division’s Superior Economies Unit
Greater rates of interest quickly would stop extra financial ache later.
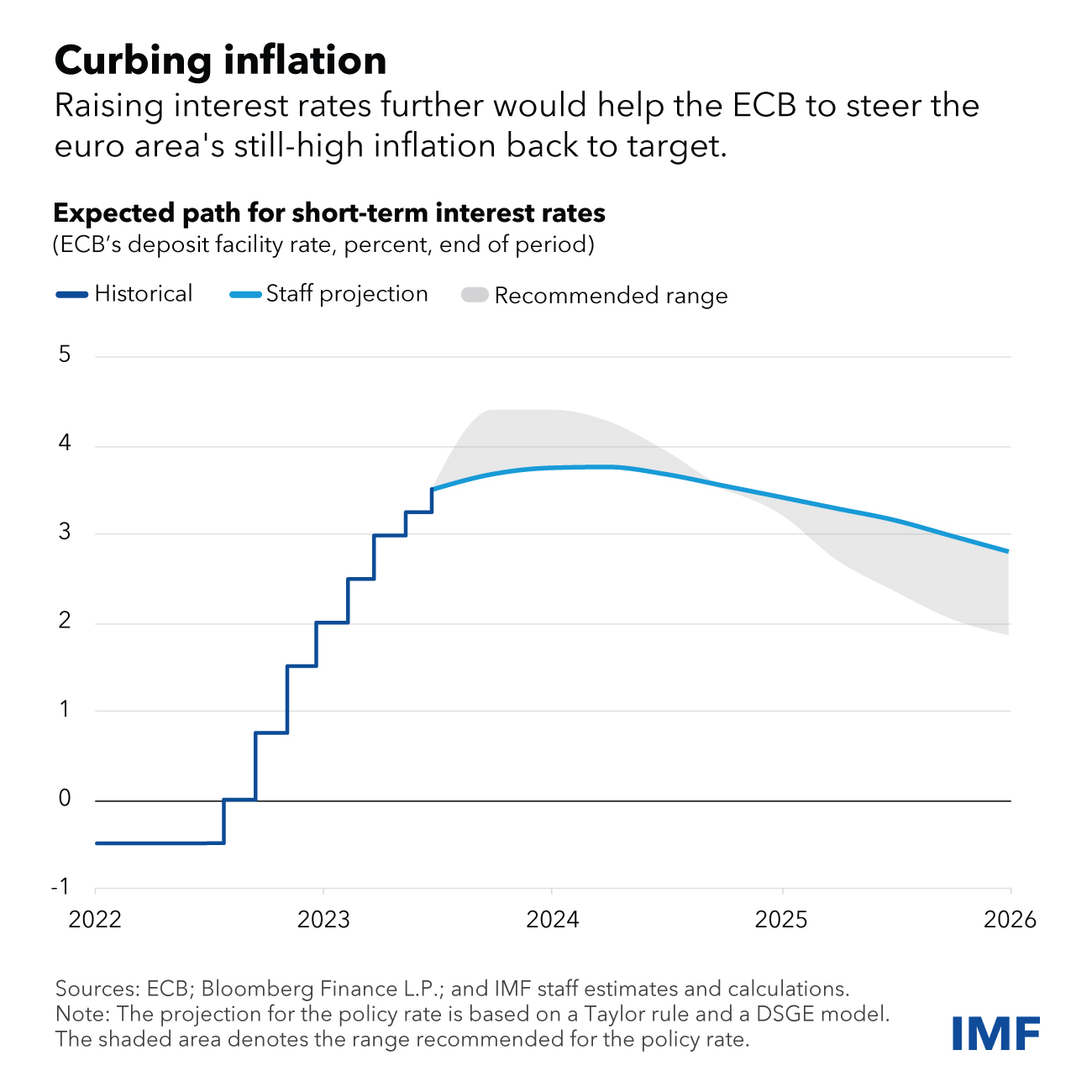
The European Central Financial institution may stop inflation expectations from changing into unmoored and drifting upwards by persevering with to boost its coverage charge, as mentioned in our current report on the euro space. An additional tightening of financial coverage within the close to time period would stop way more pricey measures later to carry inflation again to focus on.
Because the Chart of the Week exhibits, the ECB Governing Council has raised its deposit facility charge eight occasions, by a complete of 400 foundation factors, because it began to tighten coverage in mid-2022. These decisive actions have helped preserve longer-term expectations well-anchored to date.
If the ECB had been to boost its coverage charge additional and presumably above the three.75 p.c peak that markets count on now, relying on incoming knowledge, this could assist considerably to stop excessive inflation from changing into entrenched. In reality, inflation would converge extra quickly in direction of the two p.c goal and rates of interest may then fall at a sooner tempo.
The unique shocks to vitality and meals costs that catapulted inflation above goal are dissipating. However inflation remains to be excessive, with costs within the euro space rising by 5.5 p.c from a 12 months earlier in June.
Core costs – a extra dependable measure of underlying inflationary pressures – had been up by 5.4 p.c. Core inflation within the three months to June was additionally nonetheless a lot increased than the ECB’s goal, at 4.6 p.c on an annualized foundation.
Inflation pressures are prone to persist for a while. Employees will attempt to recoup losses in buying energy by pushing for increased wages, whereas companies are prone to search to guard their income by setting their retail costs to mirror increased labor prices.
We don’t see inflation coming again to focus on earlier than mid-2025 – and inflation may presumably show extra persistent if, for example, inflation expectations shift upwards or the share of wage contracts containing backward-indexation clauses will increase.
Within the face of persistent inflation, the ECB ought to persevere in maintaining financial coverage tight. For some time, the ECB ought to react extra strongly when inflation is available in above expectations than it does when inflation is beneath expectations – adopting a so-called tightening bias.
A tightening bias would assist stop excessive inflation from changing into entrenched – a foul end result that will finally drive the ECB to tighten extra and for longer to return inflation to focus on, inflicting a sharper financial downturn later.
In fact, the ECB ought to stay versatile given the financial uncertainties forward and be prepared to regulate course relying on the stream of knowledge.
The ECB’s meeting-by-meeting method to creating coverage selections rightly permits it to set charges primarily based on the evolving inflation outlook, and incoming data on the drivers of underlying inflation and the energy of financial coverage transmission.
Authentic Submit
Editor’s Word: The abstract bullets for this text had been chosen by Searching for Alpha editors.