We Indians have really imbibed the philosophy of dwelling within the current, the vartamanah, as it’s referred to as in Sanskrit. A lot in order that materials questions regarding the technique of survival within the terminal a part of life when revenue streams dwindle, scarcely bother most of us. Coverage makers too seem fairly insouciant, leading to India that includes close to the underside of the pile in old-age social safety protection.
This indifference, or maybe unwillingness, to cope with a fairly thorny problem has resulted within the retirement age in India languishing round 60 for over three a long time now; among the many lowest globally. The retirement age for central authorities staff was final revised in Could 1998, when it was moved up from 58 to 60 years. The corresponding age within the personal sector has largely been within the 58 to 62 year-band. Whereas the age was elevated for some segments the place there was scarcity of personnel corresponding to medical doctors and scientific officers, the common retirement age for India has been round 60 years for some time now.
That is regardless of the advance in healthcare services, buying energy and higher high quality of life rising longevity. The life expectancy in India in 1998 was 61.7 based on the World Financial institution. It had improved to 70.1 by 2020 with residents of some States corresponding to Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra having life expectancy properly above the nationwide common.
Whereas a number of voices have been raised in latest occasions such because the EPFO chief requesting a rise in pension age to scale back the stress of pension pay-outs and the Andhra Pradesh authorities rising the retirement age of the State authorities staff to 62, this problem has not acquired due consideration.
It is going to be good if motion is taken on this entrance quickly. Not solely will it make India lock step with different nations, there are lots of benefits from a fiscal stand level as properly.
Different nations’ expertise
Fast strides have been taken by different nations in enhancing social safety in outdated age for his or her residents. Apart from contributory pension schemes, non-contributory pension schemes in addition to social insurance coverage play an essential a part of defending the ageing inhabitants. The insurance policies framed for figuring out these schemes can’t stay insulated from the potential working age of the inhabitants.
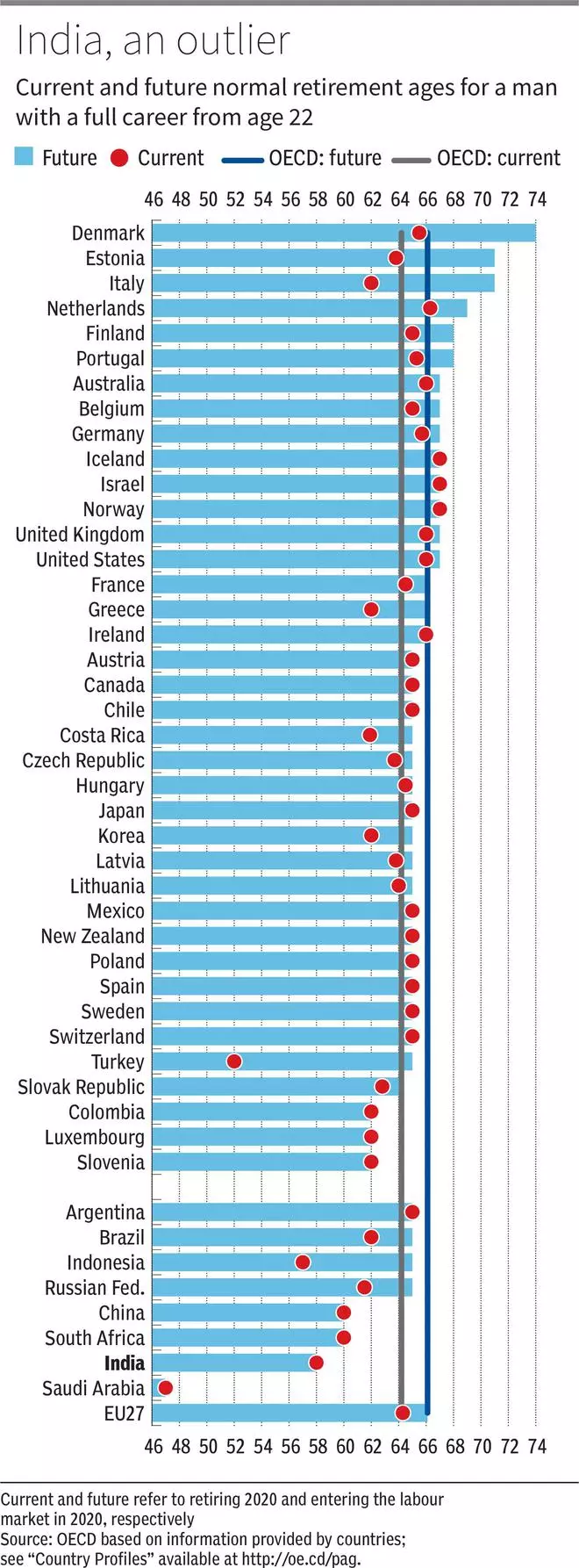
In response to OECD’s ‘Pensions at a Look 2021’ report, the worldwide common retirement age for a person working from the age of twenty-two was 64.2 years in 2020. That is anticipated to extend to 66.1 years by 2064 for individuals getting into the work drive after 2020. “In the meantime, the remaining life expectancy of males at age 65 is projected to extend on common from 18.1 to 22.5 years. So, the common enhance in males’s regular retirement ages will account for about half the common enhance in old-age life expectancy,” notes the report.
The report notes that ordinary retirement age of males will enhance in 20 out of 38 OECD nations with the very best enhance anticipated in Turkey, from 52 to 65 years. Different nations considering steep will increase in retirement ages are Denmark, from 65.5 to 74 years, Estonia, from 63.8 to 71 years and Italy, from 62 to 71 years.
There’s a robust case for rising the retirement age in India as properly. Whereas there are naysayers arguing that delaying retirement short-changes youth as there are fewer jobs to go round and promotions get delayed, these are structural adjustments which is able to get balanced through the years. Apart from the advantages of such a transfer far outweigh the disadvantages.
If we see from the social safety viewpoint, the burden on organisations and the federal government will go down by rising the retirement age in India. This enhance must be gradual, over a interval of maybe 5 years, from 60 to 65. For the reason that contributory pension has to proceed by way of the life-span of the worker, rising life expectancy has elevated the quantum of those pay-outs. Extra working years is not going to solely enhance the contributions however will even lower the pension outgo over the long term.
Additionally, because the Financial Survey 2018-19 identified, “all main States are projected to witness a decline within the share of younger inhabitants and a rise within the share of aged inhabitants over the subsequent twenty years. States forward within the demographic transition, corresponding to Himachal Pradesh, West Bengal, Maharashtra, Punjab and a lot of the southern States, would have lower than one-fourth of the inhabitants underneath the age of 20 however about one-fifth or extra inhabitants over the age of 59 by 2041.” The burden of pension payouts are, subsequently, set to maneuver larger within the coming a long time.
With pension expenditure accounting for round 5 per cent of the Centre’s complete expenditure and over 10 per cent of the expenditure of many States, the fiscal scenario will obtain a much-needed breather if the retirement age is elevated quickly. This can turn out to be useful, particularly within the subsequent couple of years, when fiscal scenario goes to be difficult.
One other profit for the exchequer is that revenue tax income will obtain a lift by way of rising retirement age because the older staff sometimes draw larger wage and therefore pay extra tax.
For easy transition
The transition is nonetheless unlikely to be easy, particularly with many worker unions underneath the misperception that the one option to make jobs accessible for the youth is by asking older staff to vacate their positions.
However dependence on these jobs wants to maneuver down within the coming years. The surge in expertise firms and start-ups and the colourful digital economic system lately has proven how it’s potential to create a number of employment choices for the educated youth within the nation.
There may be pushback from those that are mentally ready to hold up their boots at 60. The best way out may very well be to supply an choice to the staff across the present retirement age to both take voluntary retirement or to proceed working. Many organisations are already offering VRS choices for workers past a sure age. Such choices be sure that extension of working years doesn’t show burdensome to those that don’t need it. Some jobs, the place bodily exercise is required, will not be appropriate for the aged. Corporations in such segments can contemplate re-employing these past a sure age, with a unique job profile.
The advantages that older staff carry — extra expertise, dedication and loyalty — may show helpful to most organisations finally.